Executive Summary:
Enhance the business performance and boost productivity with advanced manufacturing analytics tools. This involves the smooth implementation of manufacturing analytics solutions to ensure adequate inventory management and determining production processes.
Introduction
The global big data market in the manufacturing industry is estimated to reach $9.11B by the year 2026. As technology keeps changing the industry, manufacturing companies have to understand what is meant by connected and smart manufacturing. Manufacturing can be defined as a production process where several functions are integrated to ensure that there are products that can adequately meet customers’ requirements.
Businesses can boost product quality and reduce human errors with business analytics in the manufacturing industry. In this competitive market scenario, leveraging technologies can boost data quality and accuracy. With automated manufacturing analytics, real-time data is immediately recorded during production processes. This data is used to create reports that offer valuable insights. Manufacturers can then use these insights to prevent mistakes, reduce waste, improve equipment performance, predict future problems, lower costs, and take many other beneficial actions.
What is Manufacturing Analytics?
As a key part of Industry 4.0, manufacturing analytics includes utilizing data from various sources to improve and streamline manufacturing processes. Manufacturing analytics refers to the use of statistical tools and data gathered from different sources to enhance the flow of manufacturing activities. These are data generated from the running operational platforms and systems, which facilitate the management of production processes. With the help of this data, manufacturers are to look for certain areas where it is possible to optimize the performances, thus, increasing efficiency and productivity. It also increases total organizational performance and, at the same time, reduces unwanted operating expenses, thus saving a lot.
Manufacturing analytics is indeed an integration of innovative solutions like cloud, Industrial IoT sensors, machine learning, etc. Cloud computing entails large amounts of data being stored and processed in one place and easily accessed and managed. Basically, Industrial IoT sensors gather data from mechanical devices in real time and show the performance and health condition of the equipment they are connected to. Machine learning algorithms then process this information to provide the right forecasts and enhance the decision-making processes. In combination, these technologies enable manufacturers to be more strategic, to predict and avoid problems, and to build a better production future.
Benefits and Importance of Data Analytics in Manufacturing
Data analytics in the manufacturing industry is a modern approach to analyzing and compiling data for strategic manufacturing plans. Its importance has transformed the parameters of production processes. So, let’s understand the benefits of data analytics in manufacturing to stay ahead of the competitive market.
1) Better Quality Control
Increasing the effectiveness of data analysis can greatly contribute to product quality. Manufacturers can derive key insights by collecting and analyzing data from various sources. These include sources such as sensors, making product design improvements, detecting and fixing problems earlier, and understanding what caused defects. With the product tracking system, quality is guaranteed, and you can be confident that the data you are using is reliable.
2) Supply Chain Optimization
One of the challenges business owners face is managing inventory and the supply chain, especially when there are shifts in the market. The use of the newest analytical techniques and technological advances in this area improves the visibility of the processes. This participation includes ensuring that inventory management is conducted as intended, maintaining the optimal stock levels, replenishing supplies when needs arise, planning logistic activities, engaging in predictive analysis, and risk assessment effectively.
3) Data-Driven Decision Making
Manufacturers can implement advanced tools like cloud software to integrate diverse operations for effective analysis. These tools produce insightful data from the data. The data assists in such actions as the innovation of new products, sales projection, and price fixing.
4) Manufacturing Process Improvements
In 2023, 60% of manufacturers found data analytics to be the most crucial factor in adding up to the production of 43%. Analytics tell where changes are required most. These may include such things as redundancies, flaws in the manufacturing process, or areas where there is potential for making changes. In this manner, with a complete view of the production, the manufacturer can see the actual operations and identify the section where there are issues, such as delays or cost over running, that need to be optimized.
5) Improved Productivity and Predictive Maintenance
The up-to-date operation of the devices and systems performs a significant role in contemporary manufacturing. The regular updates and remote monitoring provided by analytics tools ensure the performance is always on. IoT sensors and predictive maintenance systems send alerts to the personnel on sight in case of any predictability before the malfunction takes place, which enables planning of the maintenance and thus reduces unexpected downtimes. This increases reliability and performance and reduces unexpected maintenance expenses.
Objectives of Manufacturing Analytics
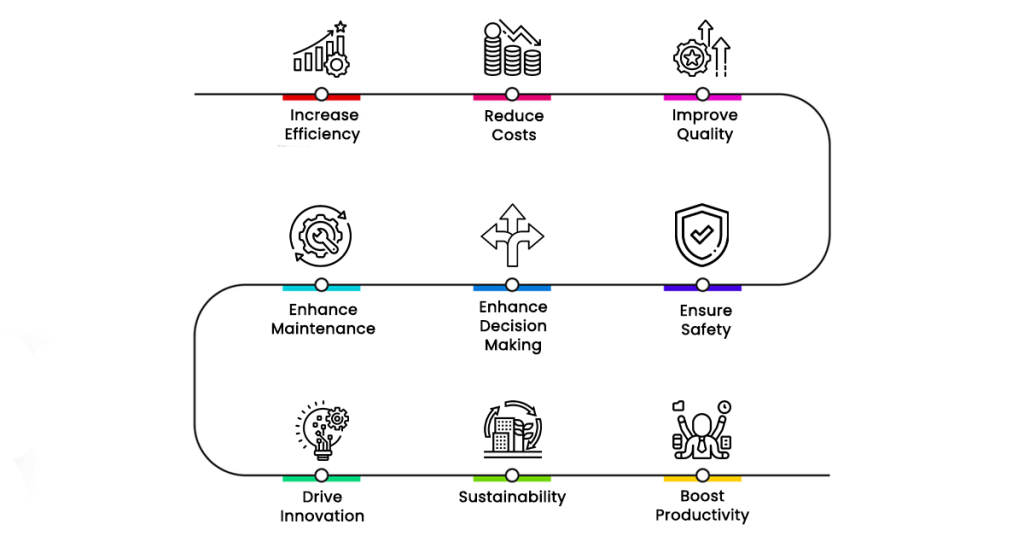
Manufacturing data analytics aims to transform crucial information into actionable data insights to drive business operations. Big data analytics in manufacturing create value for business in the following ways:
1) Increase Efficiency
Manufacturing analytics help make the production process faster and smoother. Manufacturers can determine where things are taking time and where extra effort is being used. Fixing these challenges helps boost productivity and efficiency, producing more products in less time.
2) Reduce Costs
Advanced data analytics assist in monitoring and examining whether money is being wasted or where costs are too high. Optimization methods help in lowering this by increasing resource, energy and labor utilization. They can also get rid of too many processes hence cutting on costs and improving the return of investment.
3) Improve Quality
Supervisory observation helps manufacturers identify product quality checks at an early stage of production. This assists the organization in achieving high-quality product standards and aligning abnormal products to decrease the number of complaints and increase satisfaction.
4) Enhance Maintenance
Predictive data analytics utilizes data from various equipment to predict its performance and breakdowns to reduce repair costs. This allows manufacturers to conduct maintenance processes before machine problems occur, avoiding unnecessary repair costs. When machines are maintained from time to time, they can work smoothly and raise productivity.
5) Enhance Decision-Making
The use of timely and accurate data lets one have a positive look at the production procedures. This information is used to resolve specific problems and make decisions and plans within a short span of time. Organizations such as manufacturers can prepare in advance so that when the case arises, they can handle it efficiently.
6) Ensure Safety
Tracking the status of the factories and past events can help avoid unpleasant situations. It also helps achieve a safe workplace free from accidents since employees can adhere to safety measures and recommended production processes.
7) Drive Innovation
Business analytics as an industry is dynamic, especially for manufacturing businesses. They can maintain relevancy by improving products. This assists in developing production procedures that accurately correspond to the client’s needs and expectations.
8) Sustainability
Systems and methods of effective measurement and analysis of energy consumption as well as a thorough examination of the amounts of waste produced. This helps improve the methods used in operations to decrease the effects on the environment; it also helps to conserve energy and at the same time, helps the organization build a better reputation. Sustainable practices can also lead to long-term savings and regulatory compliance.
9) Boost Productivity
By identifying areas for improvement, manufacturers can optimize the productivity of their labor, machines, and other necessary resources. This assists in enhancing the quality of final products and reducing the production time.
Discover how data analytics can transform your manufacturing process
Revolutionize Your Operations With Manufacturing Analytics
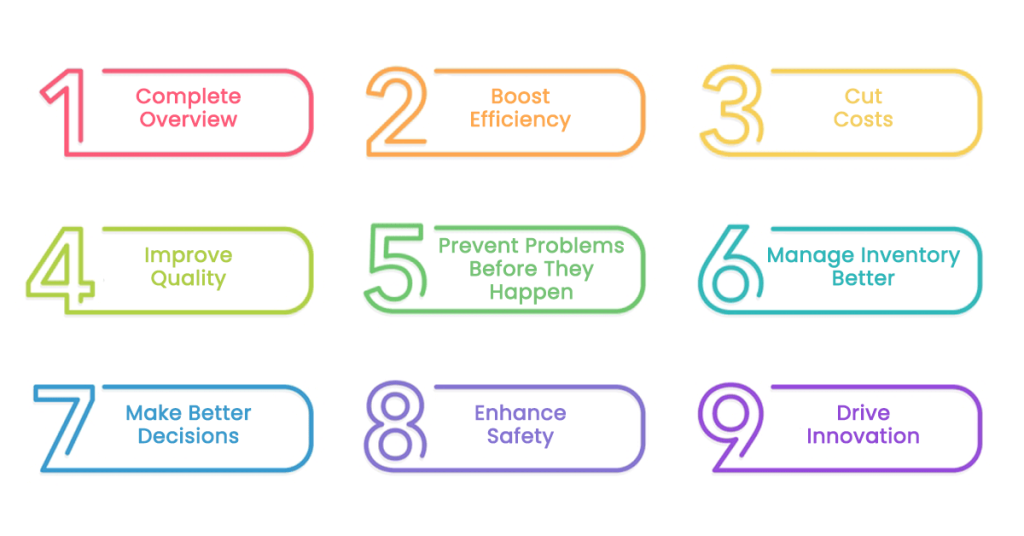
Manufacturing data analytics can transform your business operations and make them more efficient and highly functional.
1) Complete Overview
Manufacturing analytics provide a detailed picture and understanding of your production process. This helps you to track every step of the production process, from raw materials to finished products, all in one place. This clear view lets you understand what’s working well and what needs improvement.
2) Boost Efficiency
Analytics help you spot and fix slowdowns or problems in your production line. Addressing these issues makes your operations run more smoothly and faster, which ultimately leads to increasing overall efficiency.
3) Cut Costs
Data analytics in manufacturing help you find and reduce waste by analyzing how resources are used. This means you spend less on materials and production, saving money and improving your bottom line.
4) Improve Quality
Analytics tools monitor your production closely and can alert you to defects before products are finished. This helps ensure that high-quality products reach your customers.
5) Prevent Problems Before They Happen
By utilizing advanced analytics, manufacturers can predict machine performance and plan in advance when maintenance is required. This assists in predicting when the machine will break down and ensure smooth performance.
6) Manage Inventory Better
Business analytics provide data insights about inventory levels and customer demand by maintaining inventory stock. This assists in maintaining supply chain management processes by maintaining raw material inventory and final products.
7) Make Better Decisions
With real-time data and insights, manufacturers can quickly make informed decisions. Whether adjusting production schedules or planning new product launches, analytics help you make smarter, faster decisions.
8) Enhance Safety
By analyzing the safety of crucial data, you can identify potential risks and prevent accidents before they happen. This creates a safer working environment, smooth machine operations and helps comply with safety regulations.
9) Drive Innovation
Business analytics in the manufacturing industry help understand market trends and changing customer needs. This helps guide smooth development processes and improve existing products to stay competitive and responsive to changes.
Learn the key benefits and use cases of manufacturing data analytics today
Manufacturing Analytics Use Cases
Every business is different, so how you use data to create value depends on your goals and how advanced your organization’s analytics are. Modern analytics tools help eliminate gaps and silos in information and operations that can hinder growth and efficiency. Businesses can better manage key performance areas by combining data from different departments, from the order process to cash collection. This helps decision-makers boost revenue and improve profit margins by addressing important factors more effectively.
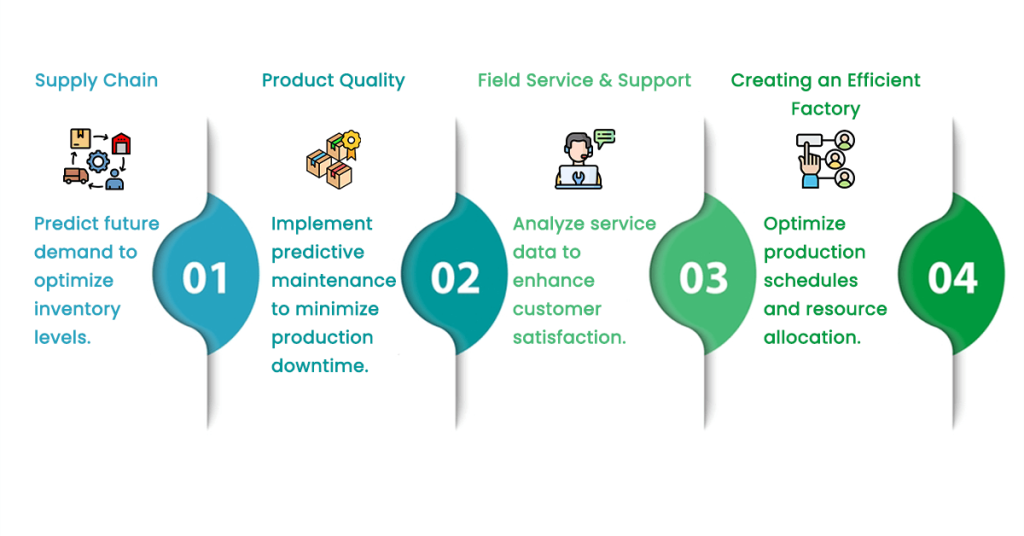
1) Supply Chain
The supply chain refers to the movement of supplier materials and final products from manufacturers to the end customer. Understanding the path ensures that companies have the right materials at the right time and lessens costs. Analytical systems function by giving advice and making predictions about possible obstacles in the process of moving materials or products.
A) Demand Forecasting
Deducting the sales of each product to estimate the product that customers will demand in the future. Forecast future demand by staying up to data with the manufacturing data to minimize data discrepancy and ensure product availability when demand arises. This ultimately assists in boosting customer satisfaction. Analytics uses historical data and market trends for trend analysis, allowing the design of relatively reliable forecasts.
B) Order Management
The process of tracking the customer’s orders from the time they are placed until they arrive at their destination. Good order management safeguards customers who have their items sent on time and as promised. Analytics introduces the means of tracking orders, the status of completion, identification of delays, and procurement of all resources needed to accomplish the whole warehouse inventory process.
B) Order Management
The process of tracking the customer’s orders from the time they are placed until they arrive at their destination. Good order management safeguards customers who have their items sent on time and as promised. Analytics introduces the means of tracking orders, the status of completion, identification of delays, and procurement of all resources needed to accomplish the whole warehouse inventory process.
C) Inventory Optimization
The correct definition of inventory optimization is the system of coordinating stock levels so that you do not overstock or tend to understock. Surplus inventory takes up both cash and storage space, while inadequate inventory levels may cause sales to stall. With the use of analytics, it is much easier to come up with the best inventory level through efficient data analysis and trend monitoring.
D) Supplier Performance
Evaluation of material suppliers on the quality, timeliness, cost fronts, and the degree of innovativeness in their deliveries. Effective control over suppliers’ performance is the key to achieving a high-quality standard and producing products promptly. Analytics control the data and track it to distinguish reliable and unreliable partners and mark areas that need improvement.
E) Transportation Analytics
The process of tracking the customer’s orders from the time they are placed until they arrive at their destination. Good order management safeguards customers who have their items sent on time and as promised. Analytics introduces the means of tracking orders, the status of completion, identification of delays, and procurement of all resources needed to accomplish the whole warehouse inventory process.
F) Early Warning Systems
Early warning systems use data to predict problems and find subsequent solutions, avoiding the consequences of adverse events. Early detection of potential issues will prevent bigger problems, saving time and money. This approach involves the discovery of common denominators and the immediate warning of parents who should take precautions.
2) Product Quality
Product quality management ensures that all products produced comply with the company’s quality standards. Receiving high-quality products encourages customers to be satisfied and come back again, and thus, fewer products will be returned. This software allows the plant to be aware of defects when they occur, measure quality, and provide better product performance.
A) Real-Time Quality Monitoring
Real-time quality monitoring means the constant checking of products during the production process.Early defect detection prevents customer complaints. Analysis by means of sensors and cameras that capture data is used to spot and promptly address the issues and potential losses.
B) Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a method used when the root cause of a problem is not known. Solving the root cause problem will prevent the same issue as above. Information technology possesses solid research on precisely what is causing the problem.
C) Reliability
Reliability deals with the allowance of the equipment and the processes of the various process machines as they work over the long term. Durable machines lower the service and the cost of the equipment. Predictive maintenance is a practice of predicting breakdowns, and regular maintenance is planned to ensure smooth operation.
D) Warranty
Handling warranty claims and examining connected details. If warranty claims are checked, the quality of the product can be increased, and future claims can be decreased. Analytics allows companies to quickly spot problems and manufacture better products.
3) Field Service & Support
The management of services like maintenance and repair for products located in the field. An effective field service saves time and maximizes satisfaction. The data analytics takes care of maintenance by creating the maintenance schedule and predicting when it will be required for repair.
A) Inventory Management
A process that ensures the sizes of an average inventory are the lowest while the customer waiting time should not be extended. Good inventory management means that products are available when needed while not staying too long in stock. The analytics software creates a balance between supply and demand, responding dynamically to changes in market conditions.
4) Creating an Efficient Factory
The adoption of methods and technologies to improve the efficiency of the factory. A factory that uses resources more efficiently will be able to produce more goods for the same money. It would also have less waste of resources. Analytics points out where the problem lies and the steps to change it.
A) Real-Time Equipment & Process Monitoring
Employing sensors and data to monitor equipment and processes without interrupting. Actual-time supervision is done in the event of any maloperation causing downtime or non-conformity. Analytics immediately gives the result on performance.
B) Process Capability
Studying the effectiveness of manufacturing processes in producing products that consistently meet standards. Every step of the operation needs to be consistent in order to ensure the very best quality products. Analytics evaluates process performance and suggests approaches to maintain consistency.
C) Optimize Maintenance
Using data for the planning and implementation of maintenance activities. Optimized maintenance means decreased downtime and maintenance costs. Evaluating the acquired data allows one to see when maintenance is required and set it soon enough.
D) OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) & Factory Productivity
The measurement of efficiency and productivity of manufacturing equipment and processes. High OEE means the factory is functioning well. Analytics pinpoints areas needing modification to be better, more productive, and reduce waste.
Conclusion
Beginning your journey with manufacturing analytics does not necessarily mean all that complicated. To start with, one should check one’s current tools and see what they are capable of as well as what they are not capable of and try to recognize some of the issues that recur. This will assist you in making a decision that meets your immediate and long-term needs and your wallet. Secondly, after identifying those willing to implement performance improvements using data analytics, create a cross-functional team to discuss how analytics can help such a business. Last, collaborate with these leaders and discover how analytics can help accomplish these primary objectives. Perhaps it may be wise to seek consultation from analytics experts about the best projects to tackle to align with its overall business objectives.