Quick Summary
Understand the concept of business intelligence and data analytics for businesses that helps in smooth decision making processes. In this blog, we will compare business intelligence and data analytics by determining its role and career opportunities. This assists in determining market trends and importance of both for smooth business operations.
This blog analyzes the contrasts between Business Intelligence (BI) and Data Analytics, focusing on their duties, benefits, and applications in present-day business situations. BI centers on changing over-organized information into significant experiences for real-time decision-making, while Data Analytics applies advanced calculations to recognize patterns and estimate the future. The point focuses on their individual roles in improving decision-making, expanding operational effectiveness, and giving prescient experiences.
It also compares professions in BI and data analytics and talks about vital devices. These contrasts make a difference for organizations to proficiently utilize information to make educated choices and obtain a competitive advantage in their industry.
What is data analytics?
Data analytics is the practice of analyzing raw data to identify patterns and answer particular queries. It includes a variety of approaches and aims specific to different businesses. This approach helps with historical trend analysis, predictive insights, and informed decision-making across many business objectives.
What is Business Intelligence?
Business Intelligence (BI) is a technology-driven process that analyzes raw information to deliver significant results. It gives administrators, managers, and workers complete viewpoints of business operations and trends. It enables them to make informed business decisions.
Business Intelligence vs Data Analytics
The conflict between Business Intelligence (BI) vs Data Analytics is common as organizations look for the finest devices for making informed decisions and driving development. In spite of the fact that these names are frequently used together, they refer to different approaches with diverse applications. The choice between business intelligence vs data analytics for small businesses can have a noteworthy effect on how productively they compete and create. Business intelligence (BI) engages large businesses, with over 33% depending on it for decision-making by 2024. In the meantime, Data Analytics improves efficiency for retailers and producers, empowering them to decrease stock levels by up to 30% through supply chain optimization. The purpose of this blog is to explore and clarify the contrasts between Business Intelligence and Data Analytics. It emphasizes their individual duties, benefits, and applications in advanced business situations.
Difference Between Business Intelligence and Data Analytics
1. Scope and Focus
BI centers on the past and the present, offering historical, current, and predicted views of corporate forms. Structured data from different sources is utilized to produce reports, dashboards, and key execution pointers (KPIs). The essential reason is to help vital decision-making by investigating past executions and distinguishing current trends.
Data analytics has a more extensive scope, counting the analysis of raw information to find designs, relationships, and patterns. It includes strategies such as factual examination, machine learning, and information mining. Data analytics works with both organized and unstructured data, looking to give noteworthy experiences and forecast future results.
2. Methods and Techniques
BI uses questioning, detailing, and online analytical processing to do descriptive analytics. It answers questions like “What happened?” and “How did it happen?” by summarizing past data. BI frameworks regularly utilize predefined measurements and KPIs to evaluate execution and monitor business insights.
Data analytics utilize complex measurable models, machine learning calculations, and predictive modeling to perform demonstrative, prescriptive, and predictive analytics. It answers questions like “Why did it happen?” and “What will happen?” by investigating more profound facts. Data analytics innovations assist businesses with more profound experiences in client behavior, market patterns, and operational efficiencies.
3. Outcome and Application
The outcomes of BI are primarily dashboards, reports, and visualizations that provide a snapshot of current or past performance. The insights are used to track business metrics and improve operational efficiency.
The outcome of Data Analytics includes predictive models, detailed analyses, and actionable insights that drive strategic decisions. It helps organizations not only understand what happened or is happening but also why it’s happening and what could happen in the future, leading to proactive decision-making.
Use Cases of Analytics and Business Intelligence
BI is used for performance monitoring, enabling organizations to track KPIs, sales trends, and financial health. For instance, retail companies use BI dashboards to monitor inventory levels and sales performance in real-time, helping to optimize supply chain management and identify top-selling products.
Data Analytics is used for predictive maintenance in manufacturing, where machine data is analyzed to predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Another use case is customer segmentation in marketing, where analytics identify patterns in customer behavior, allowing for targeted campaigns and personalized experiences.
Types of Business Intelligence
Business intelligence (BI) moves forward corporate proficiency and decision-making through the change of raw information into significant experiences. Here’s the key types of business intelligence:
1. Traditional business intelligence:
Traditional BI uses structured data from internal sources, often stored in data warehouses, and analyzed using SQL-based tools like OLAP cubes for tasks like sales analysis and financial reporting.
2. Modern business intelligence:
learn more about how business intelligence solutions might benefit your business!
Types of Data Analytics
Data analytics is crucial for modern business operations since it provides detailed experiences of a few features of organizational performance and market patterns. Here’s a look at the key types of data analytics:
1. Descriptive analytics:
Descriptive analytics focuses on summarizing historical data into key performance indicators (KPIs), providing an overview of past performance, such as sales reports or website traffic.
2. Diagnostic analytics:
Diagnostic analytics digs deeper to uncover the reasons behind past events, helping businesses understand why something happened, like customer churn or product defects.
3. Predictive analytics:
Predictive analytics leverages statistical models and machine learning to forecast future outcomes, enabling businesses to anticipate trends or risks, such as demand forecasting or fraud detection.
4. Prescriptive analytics:
Prescriptive analytics goes beyond predictions, offering actionable recommendations to optimize decisions and strategies, such as in supply chain or pricing optimization.
Benefits of Business Intelligence
1. Enhanced Decision Making
BI delivers accurate and timely data, allowing for informed decision-making. BI uses data visualization technologies to convey complicated data in simple formats like dashboards and charts. This representation allows for quick analysis of trends, patterns, and anomalies and helps in strategic planning and operational decisions.
2. Improved efficiency and productivity
BI simplifies data exploration and analysis, saving both time and resources. Automated reporting and real-time data access minimize the need for human data collection and processing. This efficiency enables staff to focus on value-added tasks, increasing total productivity while lowering operating expenses.
3. Competitive Advantage
In the BI vs DA (Data Analytics) argument, BI stands out for its ability to provide a competitive advantage through improved data visualization. Businesses can quickly recognize market patterns, competitor movement, and industry progressions. This proactive approach empowers businesses to react rapidly to showcase changes, reveal unused possibilities, and create compelling competitive strategies.
Benefits of Data Analytics
Data analytics gives a few benefits to firms by utilizing information to discover experiences and advance educated decision-making. Here are the primary benefits of data analytics:
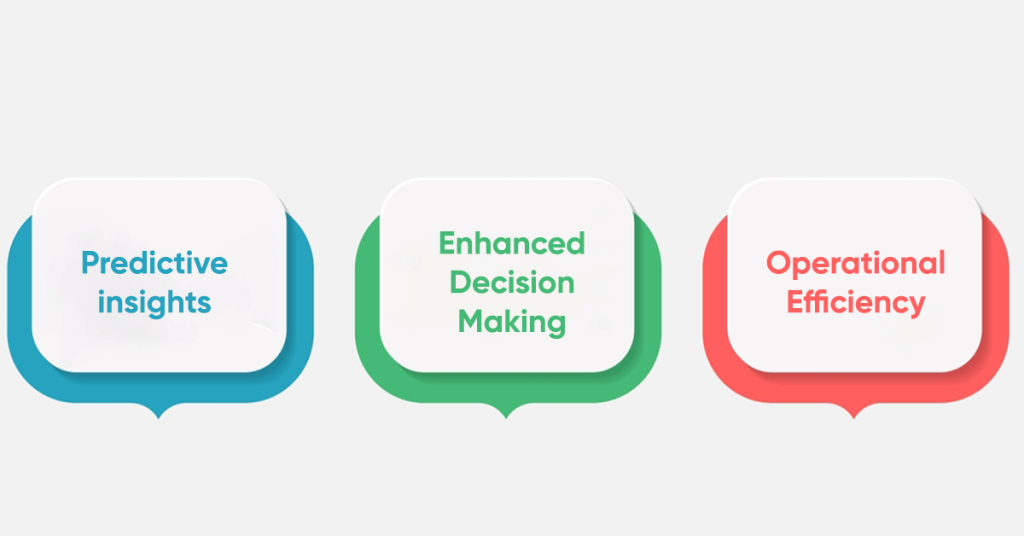
1. Predictive Insights
Data analytics empowers firms to predict future patterns by analyzing historical information. This competence encourages proactive decision-making and key planning, empowering firms to remain ahead of the competition and adjust to market developments.
2. Improved Decision-Making
Data Analytics gives significant insights that offer assistance decision-making processes through surveying enormous amounts of information. Data Analytics, as opposed to Business Intelligence (BI), which focuses on historical and present data exploration, employs progressed procedures such as machine learning and predictive modeling to reply to complicated issues and help decision-making.
3. Operational Efficiency
Data analytics empowers businesses to streamline operations and increment efficiency. Businesses can utilize operational information to identify troubles, progress operations, and cut costs. This leads to more effective resource allocation and operational performance.
Discover how data may influence your success. Contact us to learn more
Careers in Business Intelligence vs Data Analytics
Choosing between business intelligence and data analytics careers involves interacting with data to produce insights that inform company choices. Here’s a comparison between careers in business intelligence and data analytics, as well as business intelligence vs data analytics tools:
1. Careers in Business Intelligence
- BI Analyst
- BI Developer
- BI Architect
- BI Consultant
- BI Manager/Director
2. Careers in Data Analytics
- Data Analyst
- Data Scientist
- Data Engineer
- Data Architect
- Data Consultant
Transform data analysis processes with enhanced Business Intelligence tools and discover how data may influence your success.
Business Intelligence (BI) vs Data Analytics Tools
|
Business Intelligence |
Data Analytics |
|
|
Conclusion
Understanding Business Intelligence vs Data Analytics, as well as their applications, is basic for organizations looking to proficiently utilize information. Careers in Business Intelligence vs Data Analytics give various chances. Business Intelligence professions such as BI Investigator and Developer require knowledge in data visualization and SQL, but Data Analytics roles such as Data Scientist and Data Engineer require ability in programming, machine learning, and statistical analysis. In the ceaseless debate between BI vs Data Analytics, organizations ought to evaluate their individual requirements.
BI is used for operational experiences and observation, and data analytics is used for complex investigation and prescient insights. Ready to unlock the power of data? Contact us today for expert direction.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which businesses benefit most from Business Intelligence vs Data Analytics?
Business intelligence is regularly utilized in regions such as retail, banking, and healthcare to give operational announcing and observing. Data analytics is basic in businesses like e-commerce, telecommunications, and promoting client analytics and predictive modeling.
When should a business use Business Intelligence (BI) over Data Analytics?
Business intelligence is most valuable when a company requires real-time reporting, monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), and operational experiences from organized data. BI tools such as Tableau and Power BI are perfect for creating dashboards and visualizations that give an overview of current trade performance.
When should a business use Data Analytics over Business Intelligence?
Data analytics is particularly advantageous when firms are required to assess endless amounts of information, recognize complicated designs and patterns, and make expectations. Businesses can utilize Data Analytics tools such as Python, R, and SAS to embrace advanced measurable analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling in order to inform key choices and drive innovation.